Have you ever wondered how your ears work? How do they pick up sounds and turn them into something you can understand? Imagine this: you’re at a crowded party, surrounded by people talking, music blaring, and glasses clinking. Despite the chaos, you are able to hear your friend’s voice clearly as they tell you a story. How is that possible?
In this article, we will take a journey through the inner ear to explore the intricate workings of our hearing system. From the cochlea to the semicircular canals, we will delve into each part of the labyrinthine structure that allows us to perceive sound. Along the way, we will also examine common hearing problems and ways to protect your precious sense of hearing. So sit back and get ready for an adventure into one of our most remarkable senses – hearing!
The Basics of Hearing
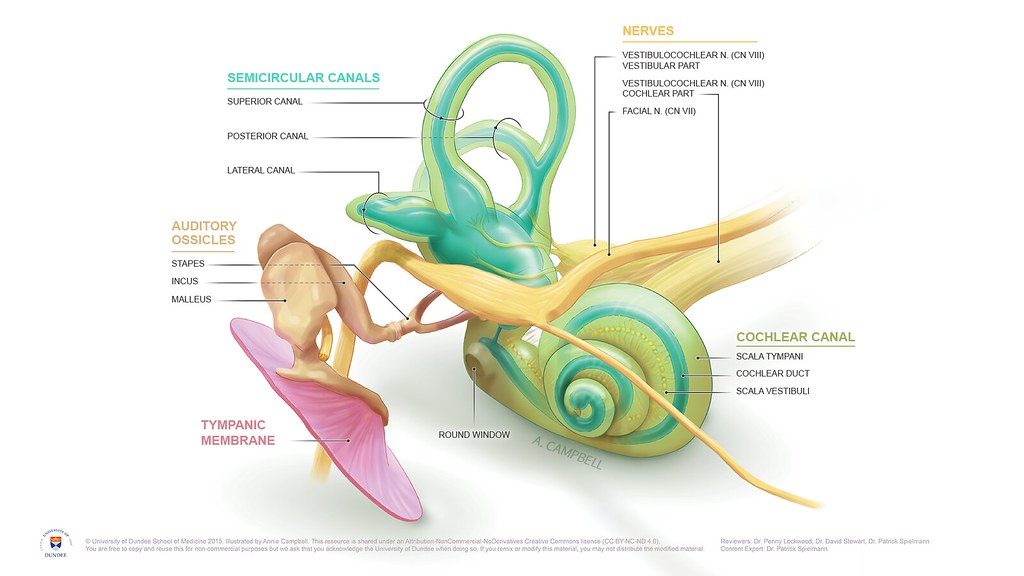
You’ll quickly grasp the fundamentals of how we perceive sound and interpret it as speech or music. It all starts with sound waves, which travel through the outer ear and into the ear canal. The waves cause vibrations in the eardrum, which then move tiny bones in the middle ear called ossicles. These movements amplify the vibrations before they are sent to the inner ear.
The inner ear is made up of a complex system of fluid-filled canals and chambers called the labyrinth. Here, specialized hair cells detect and convert these amplified vibrations into electrical signals that are sent to the brain for interpretation as sound. However, exposure to loud noises or certain medications can damage these delicate hair cells, leading to hearing loss. To prevent this from happening, it’s important to protect your ears from excessive noise by using earplugs or earmuffs when necessary.
Without proper care and protection, hearing loss can become a serious problem that affects your daily life. Fortunately, there are many ways to prevent this from happening and maintain good hearing health throughout your lifetime. As we delve deeper into the inner workings of the ear, we will explore how one part in particular -the cochlea- plays a crucial role in our ability to hear different frequencies of sound.
The Cochlea
As you delve deeper into the inner ear, you’ll come across the cochlea. This spiral-shaped organ is responsible for translating sound waves into electrical signals that can be sent to your brain for processing. Its intricate anatomy and complex function make it a fascinating subject of study in the field of audiology.
Anatomy and Function
The complex workings of our ability to hear can be explored by understanding the intricate structures and processes of this fascinating part of the human body. The anatomy and function of the inner ear are crucial in comprehending how we perceive sound. This part of the ear is responsible for converting sound waves into electrical signals that can be interpreted by the brain.
To further delve into this topic, here are two sub-lists to engage you:
- Anatomy:
- The three main components of the inner ear are the cochlea, vestibule, and semicircular canals.
- The cochlea is a spiral-shaped structure filled with fluid and lined with tiny hair cells that vibrate in response to incoming sound waves.
- Function:
- Sound waves enter through the outer ear and travel through the middle ear, causing vibrations in the eardrum.
- These vibrations move small bones in the middle ear, which ultimately stimulate hair cells in the cochlea to send electrical signals to the brain.
Understanding this vital process allows us to appreciate how miraculous our sense of hearing truly is. Moving forward, we will explore how these electrical signals are translated into meaningful sounds that we can comprehend.
How Sound is Translated into Electrical Signals
Let’s explore how our brain turns sound waves into electrical signals that we can interpret and understand. When sound enters the ear, it causes the eardrum to vibrate, which in turn moves three tiny bones in the middle ear. These bones amplify and transmit the vibrations to the inner ear, where they are detected by hair cells within the cochlea.
The hair cells are responsible for transducing mechanical energy from sound waves into neural signals that can be interpreted by the brain. Each hair cell is tuned to a specific frequency of sound, and when it detects a vibration at its designated frequency, it sends an electrical signal along its auditory nerve fiber. This process is known as neural encoding and ultimately leads to our perception of sound. To illustrate this process further, consider this table:
| Sound Frequency | Hair Cell Response | Auditory Nerve Fiber Activity |
|---|---|---|
| 1 kHz | High | High |
| 2 kHz | Low | Low |
| 3 kHz | Medium | Medium |
As you can see from the table above, different frequencies of sound cause different responses in hair cells and affect their corresponding auditory nerve fibers differently. Understanding this complex mechanism allows us to appreciate just how intricate our hearing system truly is. Moving forward, let’s delve deeper into the vestibule and discover more about its role in our ability to hear sounds accurately without feeling dizzy sensations like vertigo or imbalance while moving around.
The Vestibule

You’ll feel like you’re stepping into a magical world as you enter the vestibule, where your balance control and spatial orientation are first put to the test. The vestibule is a small chamber located within the inner ear that contains two important structures: the utricle and saccule. These structures are responsible for detecting linear acceleration and head position in relation to gravity.
The utricle is positioned horizontally while the saccule is positioned vertically. Both structures contain hair cells that respond to movement by generating electrical signals that travel to the brain via the vestibular nerve. This information helps us maintain our balance, stabilize our gaze during head movements, and coordinate our movements with visual input.
As you continue your journey through the inner ear, you’ll encounter another fascinating structure called the semicircular canals. These three fluid-filled tubes are oriented perpendicular to each other and detect rotational movement of the head. Together with the utricle and saccule, they form an intricate system of sensors that allows us to perceive our position in space and move through it with ease.
The Semicircular Canals
As we journey deeper into the labyrinthine world of our inner ear, the semicircular canals appear like three fluid-filled tubes that detect rotational movement. These bony structures are responsible for our vestibular function, or our sense of spatial orientation and balance control. Each canal is positioned at a right angle to one another and contains hair-like sensors called hair cells.
When you move your head, the fluid inside the semicircular canals also moves, and this motion stimulates the hair cells. The information from these hair cells is then sent to the brain via the vestibular nerve. This allows us to maintain balance while walking or running, as well as keep track of changes in body position.
The role of the semicircular canals in maintaining balance cannot be overstated. They work seamlessly with other parts of our inner ear and nervous system to provide constant feedback about our orientation in space. In fact, disruption to this system can result in dizziness or vertigo, making it clear just how important these delicate structures are for everyday life. Moving forward, we will explore how hair cells play a crucial role in this process.
The Role of Hair Cells
You can better understand how your body maintains balance by learning about the crucial role that hair cells play in detecting motion and sending signals to your brain. Hair cells are located within the ear’s sensory organs, where they sense vibrations caused by sound waves or head movements. They work hand-in-hand with the semicircular canals to maintain equilibrium.
But what happens when these tiny hair cells become damaged? Unfortunately, unlike other parts of the body, hair cell regeneration is limited in humans. Once destroyed, they do not grow back. But there’s hope on the horizon as researchers continue to explore ways to repair or replace these essential sensory receptors.
Despite their fragile nature, hair cells are integral players in our hearing and balance systems. Understanding their importance sheds light on how we perceive sound and movement. Now that you have a better grasp of their function and limitations, let’s delve into the auditory pathway and see how information travels from your ears to your brain.
The Auditory Pathway
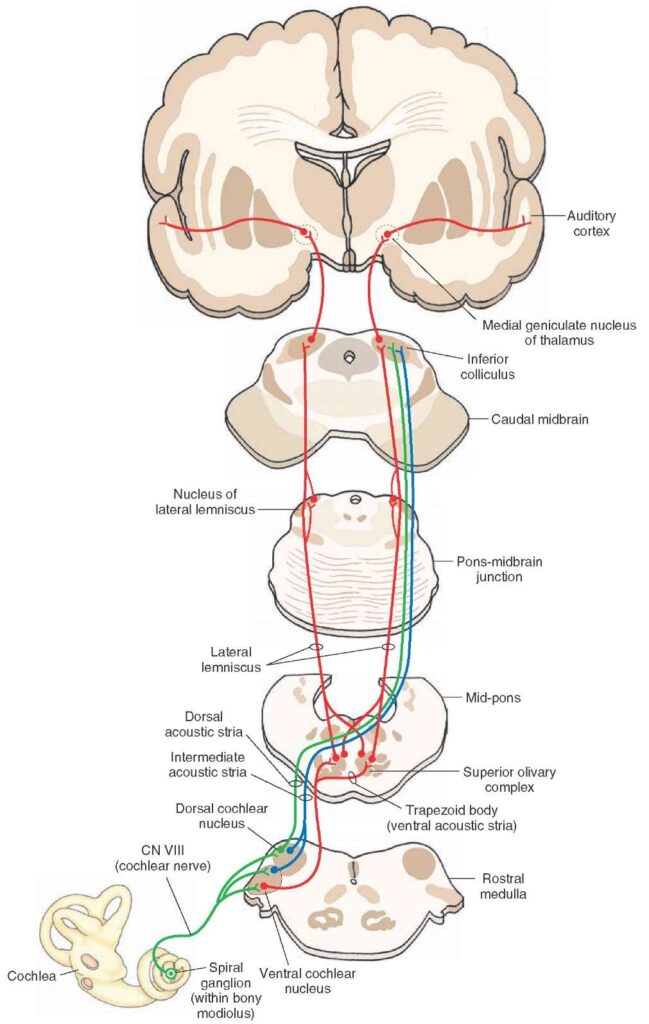
Now that you have an understanding of the role hair cells play in hearing, let’s delve into how sound signals are processed in the brain. This process is crucial for interpreting and comprehending auditory information. Timing and localization are also important factors in this pathway, as they aid in pinpointing the exact location of a sound source. Together, these factors allow us to hear and comprehend the world around us with accuracy and precision.
How Sound Signals are Processed in the Brain
Our brains process sound signals in a fascinating way, demonstrating brain plasticity and leading to our auditory perception. Our auditory system has the ability to adapt and change based on its environment. For example, individuals with hearing loss may experience changes in their brain that allow them to better perceive speech sounds over time.
The processing of sound signals involves complex neural pathways that help us identify where sounds come from and what they mean. This includes areas of the brain responsible for analyzing different aspects of sound, such as frequency and intensity. The brain then integrates this information into a cohesive interpretation of the world around us. The importance of timing and localization in this process cannot be overstated, as it allows us to distinguish between different sources of sound and understand speech even in noisy environments.
The Importance of Timing and Localization
As you listen to the world around you, your brain seamlessly processes timing and localization information. This allows you to perceive the location and distance of sounds as well as their timing relative to each other. The importance of binaural cues in sound localization cannot be overstated. Binaural cues are differences in sound intensity, phase, and arrival time between the two ears that help us determine where a sound is coming from.
Unfortunately, hearing loss can greatly impact the ability to accurately process timing and localization information. In fact, one of the earliest signs of hearing loss is difficulty with understanding speech in noisy environments due to an inability to separate important auditory signals from background noise. This highlights just how critical good hearing health is for maintaining accurate auditory perception and overall quality of life. As we move into discussing common hearing problems, it is important to remember that even minor hearing difficulties should not be ignored or dismissed as unimportant.
Common Hearing Problems

You may encounter several issues related to your ability to hear, such as tinnitus or age-related hearing loss. Tinnitus is a condition where you hear ringing or buzzing in your ears, even when no external sound is present. It can be caused by exposure to loud noise, ear infections, or certain medications. While there is no cure for tinnitus, there are treatments available like cognitive behavioral therapy and sound therapy that can help manage the symptoms.
Age-related hearing loss is another common issue that many people experience as they get older. As we age, our inner ear structures naturally deteriorate which leads to a gradual decline in our ability to hear high-pitched sounds and understand speech. Hearing aids are often used as an effective solution for this type of hearing loss. These devices amplify sounds and make them easier to distinguish so you can better understand conversations and enjoy music again.
In addition to these two common problems, there are other types of hearing disorders such as conductive hearing loss and sensorineural hearing loss that require medical attention from an audiologist or ENT doctor. However, with proper treatment options available for most cases of hearing impairment, it’s important not to ignore any signs of potential issues with your hearing. With the right approach, you can improve your quality of life significantly by addressing any underlying problems that may be affecting your ability to hear properly.
As you consider ways to protect your ears from damage caused by noise exposure moving forward into the subsequent section about ‘hearing protection’, keep in mind that prevention is always better than treatment when it comes to preserving your sense of hearing over time. By taking steps like wearing earplugs at concerts or using noise-canceling headphones when working in loud environments like construction sites or airports, you can reduce your risk of developing both temporary and permanent forms of noise-induced hearing loss down the line.
Hearing Protection

Don’t let noise rob you of your ability to hear the world around you – take control and protect your hearing with these simple yet effective tips. Hearing protection is essential for anyone exposed to loud noises on a regular basis, whether it be at work or during recreational activities. Noise exposure management can help prevent hearing loss, tinnitus, and other auditory problems caused by prolonged exposure to loud sounds.
The first step in hearing protection is to identify potential sources of noise exposure. This may include industrial machinery, power tools, firearms, live music performances, or even everyday traffic noise. Once identified, it’s important to take steps to reduce or eliminate exposure as much as possible. This may involve wearing earplugs or earmuffs while working or attending concerts, turning down the volume on personal music devices, or taking breaks from noisy environments.
In addition to reducing noise exposure levels, proper use of hearing protection equipment is crucial for maximum effectiveness. Earplugs should be inserted correctly and snugly into the ear canal while earmuffs should fit securely over both ears without any gaps. Regular cleaning and maintenance of hearing protection equipment also ensures optimal performance over time. By following these simple guidelines for hearing protection and noise exposure management, you can safeguard your ability to hear well into the future.
By implementing these measures in day-to-day life and prioritizing your auditory health through conscious choices regarding sound exposure levels and protective measures like earplugs and earmuffs when necessary; you can effectively manage your hearing abilities long-term without unnecessary risk of damage due to excessive noise pollution in our modern world full of constant stimulation from all angles we must remain vigilant about protecting ourselves from harmful decibels that can impact our quality of life if left unchecked.
Conclusion

As we conclude our discussion on hearing protection, it’s important to consider the wonder of the human body’s capabilities when it comes to hearing. The inner ear plays a crucial role in this process, converting sound vibrations into electrical signals that the brain can interpret. Despite its complexity, our bodies are able to perform this function effortlessly and automatically, highlighting the remarkable nature of human physiology.
Summary of Inner Ear Function
The summary of how the ear functions provides a comprehensive understanding of auditory perception. The inner ear, consisting of the cochlea and vestibular system, plays a crucial role in converting sound waves into electrical signals that travel to the brain for interpretation. Here are some key components and functions of the inner ear:
- Cochlea: This spiral-shaped organ contains thousands of tiny hair cells that convert sound vibrations into electrical impulses.
- Vestibular System: This helps us maintain balance by detecting head movements and sending signals to the brain about our spatial orientation.
- Eustachian Tube: This connects the middle ear to the back of your throat and helps regulate air pressure in your ears.
- Auditory Nerve: This nerve carries electrical signals from the hair cells in your cochlea to your brain for processing.
Understanding how these components work together can help you appreciate just how amazing our hearing capabilities truly are. As we delve deeper into this topic, we will explore more about the wonder of the human body’s capabilities.
The Wonder of the Human Body’s Capabilities
Get ready to discover the mind-blowing abilities of our incredible bodies! The wonders of the human body’s capabilities are truly amazing, and the marvels of evolution can be seen in every aspect of our hearing. Our ears have evolved over millions of years, and they are capable of detecting sounds that range from the quietest whisper to the loudest explosion.
Despite their astonishing abilities, there are limits to human hearing. The range that we can hear is limited by both frequency and volume. We may not be able to hear everything, but what we can detect is still an incredible feat. With each passing day, scientists continue to uncover new information about how our inner ear works, allowing us a deeper understanding and appreciation for one of the most complex systems in our body.
Frequently Asked Questions
How does hearing loss affect the brain?
Imagine waking up one day, unable to hear the voices of your loved ones or the sounds of nature around you. This is the reality for millions of people suffering from hearing loss. But did you know that hearing loss doesn’t just affect our ears, but also our brains? Brain plasticity allows our brains to adapt and reorganize in response to changes in sensory input. However, when there is a lack of auditory stimulation due to hearing loss, this can lead to cognitive decline and an increased risk for dementia. It’s not just about missing out on conversations – hearing loss can have a profound impact on our overall health and well-being.
Can hearing loss be reversed?
If you are suffering from hearing loss, you may be wondering if there is a way to reverse the damage. Thanks to advances in regenerative medicine and gene therapy, researchers are exploring new ways to restore hearing function. Regenerative medicine focuses on using stem cells or other materials to replace damaged tissues within the ear. Gene therapy involves introducing healthy genes into cells that have been damaged by genetic mutations. While these treatments are still in the experimental stages, there is hope that they could one day lead to a cure for hearing loss. However, it’s important to note that not all types of hearing loss can be reversed and some may require alternative treatments such as hearing aids or cochlear implants.
What impact does noise pollution have on hearing?
Exposure to excessive noise pollution can have a significant impact on your hearing health. Prolonged exposure to loud noises, such as traffic or industrial machinery, can damage the delicate hair cells in your inner ear and lead to permanent hearing loss. To prevent this from happening, it is important to take steps to manage and reduce noise pollution in your environment. This may include using noise-cancelling headphones, limiting exposure to loud sounds, or investing in soundproofing materials for your home or workplace. Additionally, reducing noise pollution can have positive effects on overall health, including improved sleep quality and reduced stress levels. Taking proactive measures now can help protect your hearing and ensure a healthier future.
Are there any natural remedies for hearing loss?
Looking for a natural way to improve your hearing? You might consider trying herbal supplements or home remedies. Some people claim that certain herbs, like ginkgo biloba and ginger, can help with hearing loss by improving blood flow to the ears. Others suggest using garlic oil drops or onion juice as a home remedy. However, it’s important to note that there is limited scientific evidence supporting these claims. It’s always best to talk to your doctor before trying any new supplement or remedy, especially if you have an existing medical condition or take other medications.
How does hearing loss affect mental health?
If you are experiencing hearing loss, it can have a significant impact on your mental health. Social isolation is a common issue for those with hearing loss, as communication becomes more difficult and they may feel left out of conversations or events. This can lead to feelings of loneliness, depression, and anxiety. Coping mechanisms such as seeking support from loved ones or joining support groups can be helpful in managing these emotions. It’s important to remember that hearing loss does not define you and there are resources available to help improve your quality of life.
Conclusion
Congratulations! You’ve made it through the hearing labyrinth and gained a deeper understanding of how your inner ear works. You now know that the cochlea, vestibule, and semicircular canals all play crucial roles in processing sound and maintaining balance. The hair cells within these structures are delicate and easily damaged, so it’s important to take steps towards protecting your hearing.
By wearing earplugs in noisy environments or limiting exposure to loud noises, you can prevent common hearing problems like tinnitus or noise-induced hearing loss. Remember, an ounce of prevention is worth a pound of cure! So keep those headphones at a reasonable volume and give your ears a break every once in a while.
As they say, knowledge is power. By learning about the intricacies of your inner ear, you can better appreciate the amazing capabilities of this complex system. So whether you’re listening to music or simply trying to maintain your balance on uneven ground, take care of your ears and enjoy all the sounds life has to offer!